Objective: This study intends to investigate the prognostic risk factors of bloodstream infection in Beijing.
Methods:
This study is a clinical retrospective study. Four hundred forty-six
patients with community-onset bloodstream infections (COBSI), admitted
to the emergency department and inpatient department of Beijing
Jishuitan Hospital from January 1, 2015, to December 31, 2019, were
selected as the main research objects. According to whether the patient
survives for 100 days or not, 363 cases were in the survival group, and
83 cases were in the death group. By analyzing the clinical data of the
two groups of patients, the epidemiology, clinical characteristics,
bacterial resistance, and risk factors affecting the prognosis of the
patients were analyzed.
Results:
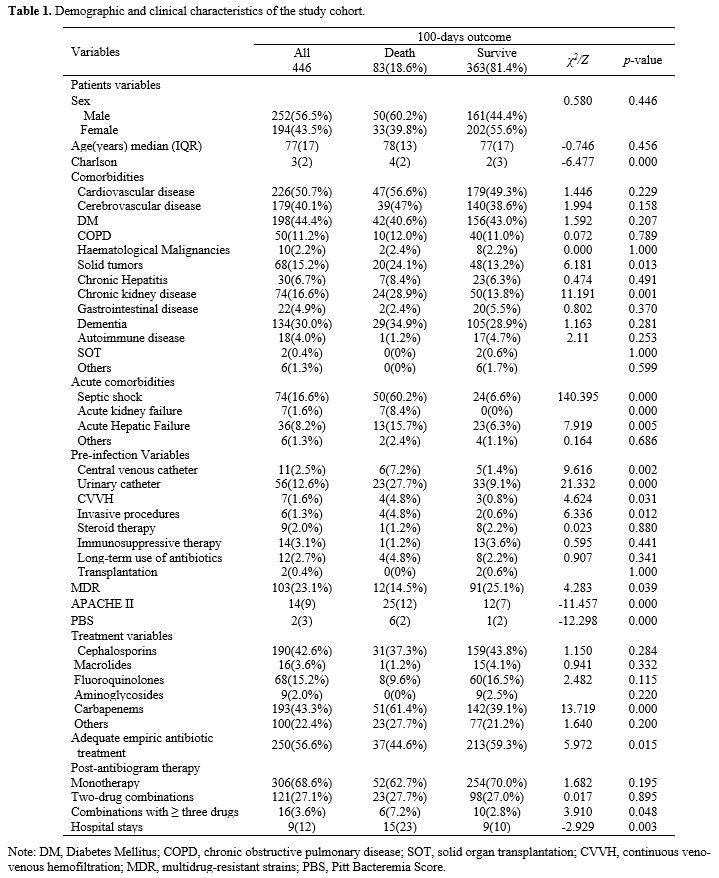
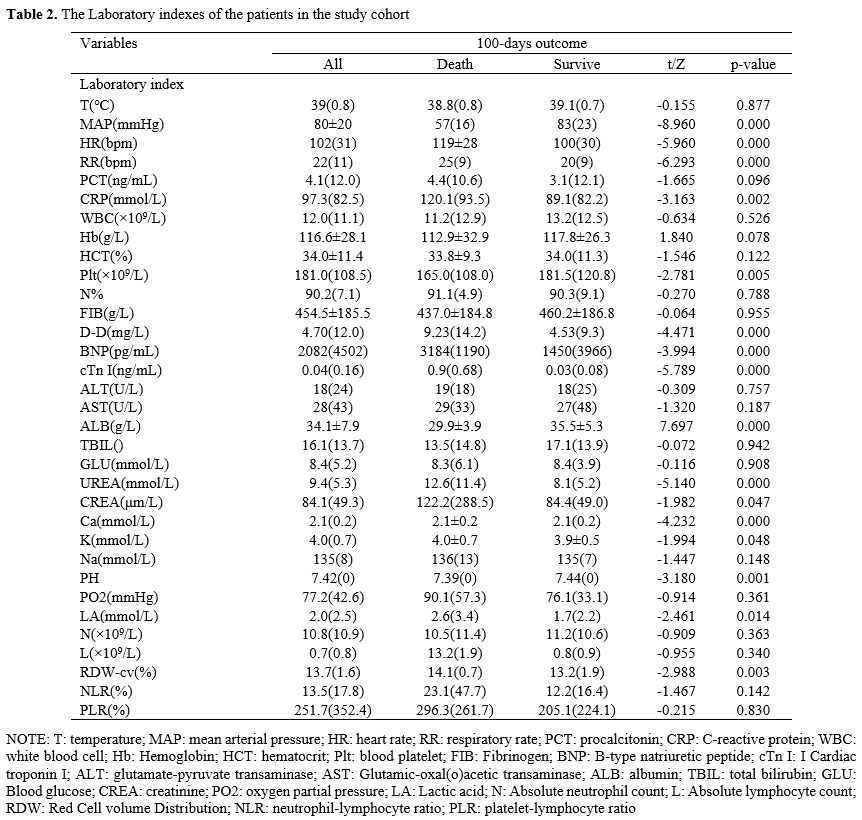
A total of 446 pathogenic bacteria were isolated in this study,
including 324 Gram-negative (G-) bacteria (72.6%), 121 Gram-positive
(G+) bacteria (27.1%). The results of the study showed that there were
significant differences in MDR, initial antibiotic use, solid tumor,
CKD, septic shock, acute liver injury, AKI, central venous catheter,
urinary catheter, blood replacement therapy, invasive operation, and
use of three or more antibiotics between the two groups (p<0.05).
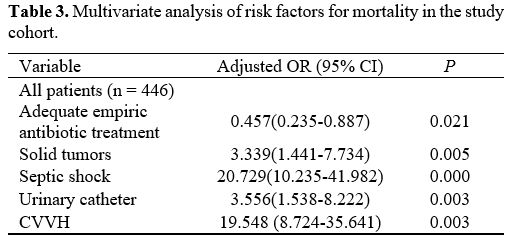
The multiple logistic regression analysis showed that solid tumors
(OR=3.339, 95% CI: (1.441, 7.734), p=0.005), combined septic shock
(OR=20.729, 95% CI: (10.235, 41.982), p<0.001), indwelling catheters
(OR=3.556, 95% CI: (1.538, 8.222), p=0.003) and continuous venovenous
hemofiltration (CVVH, OR=19.548, 95% CI: (8.724, 35.641), p=0.003) are
independent risk factors affecting the prognosis of COBSI patients.
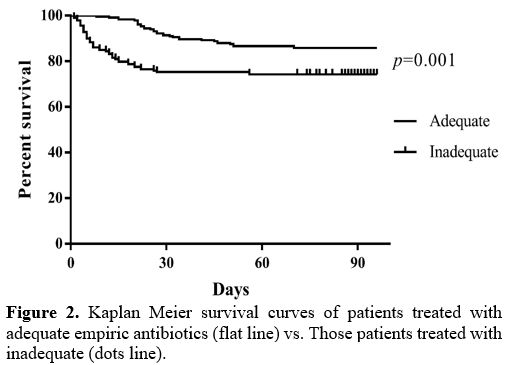
Appropriate initial antibiotic therapy is a protective factor affecting
the prognosis of COBSI patients.
Conclusion:
Solid tumors, combined septic shock, indwelling catheters, CVVH are
independent risk factors affecting the prognosis of COBSI patients.