Our first aim is to investigate if there are diagnostic features derived from morphology, cytogenetics, epigenetics, and molecular studies in the present literature, favoring the diagnosis of de novo or therapy-related MDS. If this possibility does not exist, it is logical to conclude that t-MDS should be considered a special subgroup of MDS.
Considering the importance of the morphology in MDS diagnostics, the first question could be if the morphology and the subtypes of MDS are different in de novo versus therapy-related MDS. Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome is generally classified according to morphologic schemes used for de novo MDS.[5] Different studies agree that there are no substantial differences in morphology between de novo and therapy-related MDS.[5,6] However, the morphologic subclassification of t-MDS, based on the percentage of blasts, may not be clinically relevant.[7] A study of the Chicago group found no differences in 81 patients with therapy-related MDS concerning median survival times among patients classified into the different WHO subgroups of MDS or taking into account their bone marrow blast percentage; these results indicate a uniformly poor outcome in t-MDS regardless of morphologic classification.[7] The cytogenetic stratification by the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) guidelines or karyotypic complexity was prognostically significant, independently from the bone marrow blast number. This datum was fundamental to classifying t-AML and t-MDS in the same group of therapy-related myeloid neoplasm.[1] However, it was not confirmed by a more recent study derived from a database of MD Anderson Cancer Center and Massachusetts General Hospital, including 660 patients who met the strict WHO criteria for t-MN after excluding 137 patients with >30% blast in the bone marrow. In this group, a blast percentage >5 was an independent risk factor of a bad prognosis.[8]
The group of therapy-related neoplasm includes MDS and AML post-chemotherapy, post-radiotherapy, and possibly post-benzene. According to some reports, the behavior of these last neoplasms could be like de novo ones. The drugs more frequently associated with the insurgence of MDS are reported in table 1.
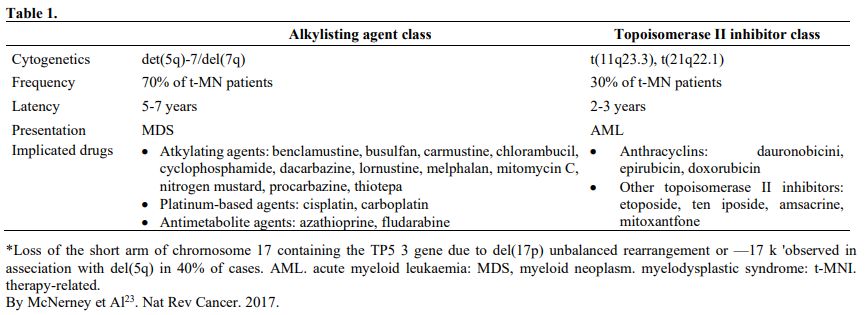 |
Table 1 |
Nardi et al.,[5] studying three groups of MDS patients, primitive, radiotherapy related (XRT), and chemotherapy-related (C/CMT), showed that the distribution of MDS types according to the WHO Classification for non–therapy-related (primary) MDS and the blood counts at presentation were similar among the three groups. Only 27% of the XRT patients had intermediate-2 or high IPSS scores, compared with 60% of the C/CMT patients. Patients in the XRT group had IPSS scores significantly lower than the C/CMT patients p<.001) but similar to the de novo (p-MDS) MDS/CMML patients. These authors conclude that patients with t-MN after XRT alone had a superior overall survival (p < .006) and a lower incidence of high-risk karyotypes (p <.01 for AML and < .001 for MDS) compared with patients in the C/CMT group. (Table 2)
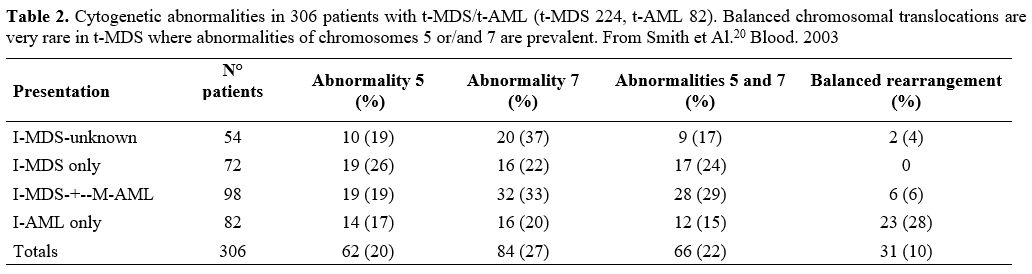 |
Table 2. Cytogenetic
abnormalities in 306 patients with t-MDS/t-AML (t-MDS 224, t-AML 82).
Balanced chromosomal translocations are very rare in t-MDS where
abnormalities of chromosomes 5 or/and 7 are prevalent. From Smith et
Al.[20] Blood. 2003 |
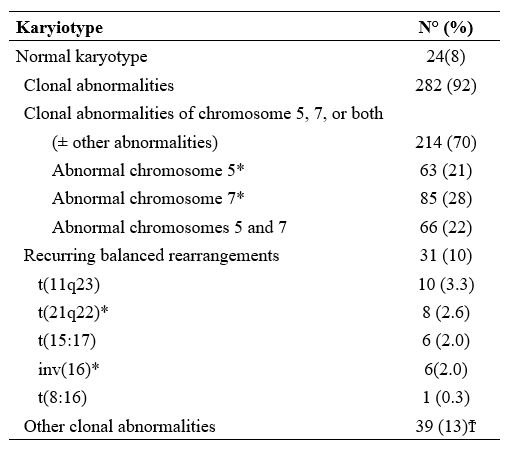 |
In contrast, there were no significant differences in survival or frequency of high-risk karyotypes between the XRT and de novo groups. AML and MDS diagnosed in the past decade in patients after receiving XRT alone differ from t-MN occurring after C/CMT and share genetic features and clinical behavior with de novo AML/MDS. These results suggest that post-XRT MDS/AML may not represent a direct consequence of radiation toxicity and warrant a therapeutic approach similar to de novo disease. Similarly, the MDS secondary to benzene (Bz) also seems to have characteristics not similar or identical to t-MDS/AML, as supposed in the past.[11,12]
Irons et al.[12] recently studied the prevalence of hematopoietic and lymphoid diseases for 2,923 consecutive patients prospectively diagnosed in their laboratory in Shanghai utilizing World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. The Shanghai series of 722 cases of AML includes the most extensive published series with documented Bz exposure and 644 unexposed de novo-AML cases. They also reported the clinical, phenotypic, and molecular characteristics of MDS developing in 649 patients, of whom 80 were determined to have some Bz exposure. In as much as t-MDS and t-AML are considered to be overlapping entities, they initially were surprised to discover that MDS presenting in individuals with chronic exposure to Bz at high concentrations (67–100 mg/m3) did not exhibit a pattern of cytogenetic and phenotypic abnormalities typically observed in t-MDS. In fact, in their MDS series, cases associated with exposure to the highest concentrations of Bz (n 5 29) were found to have a lower prevalence of clonal cytogenetic abnormalities (24%) when compared with unexposed, that is, p-MDS cases (30%) (n 5 569). Further, they did not observe an increase in clonal deletions involving all or part of chromosomes 5 or 7 in Bz-exposed MDS relative to unexposed MDS cases and in no instance involving 5/5q- as the sole abnormality. The conclusion was that benzene exposed MDS-Leukemia patients more closely resemble de-novo than therapy-related MDS leukemia.
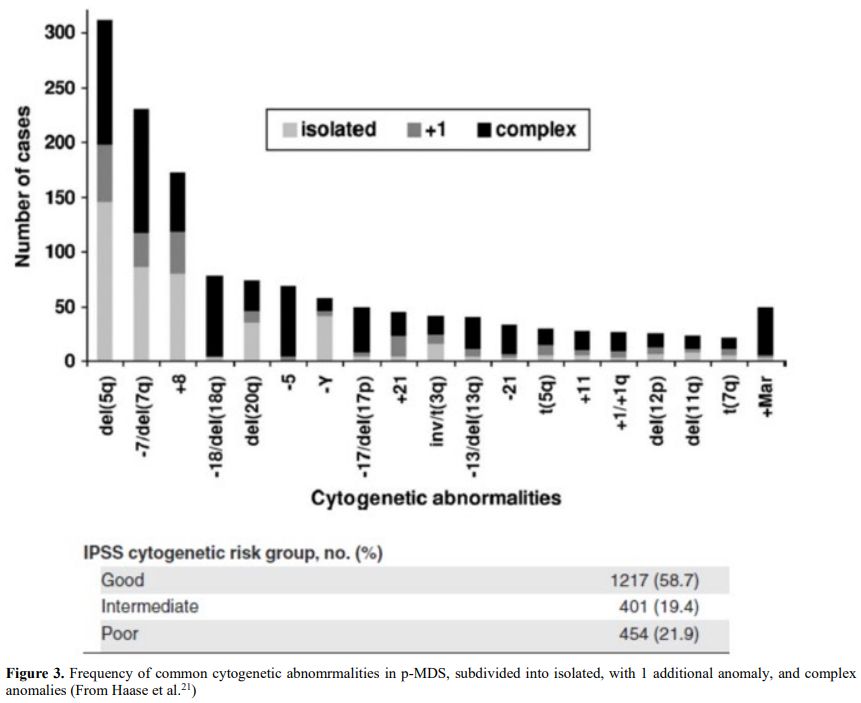
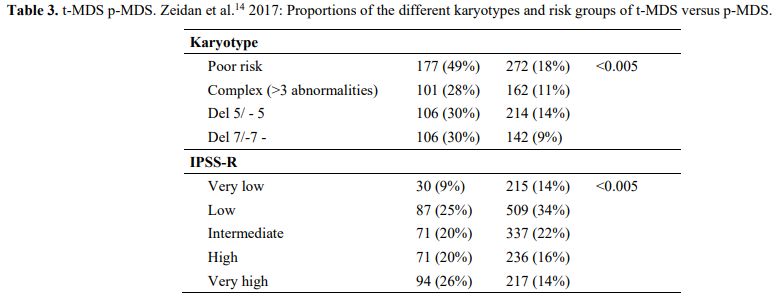
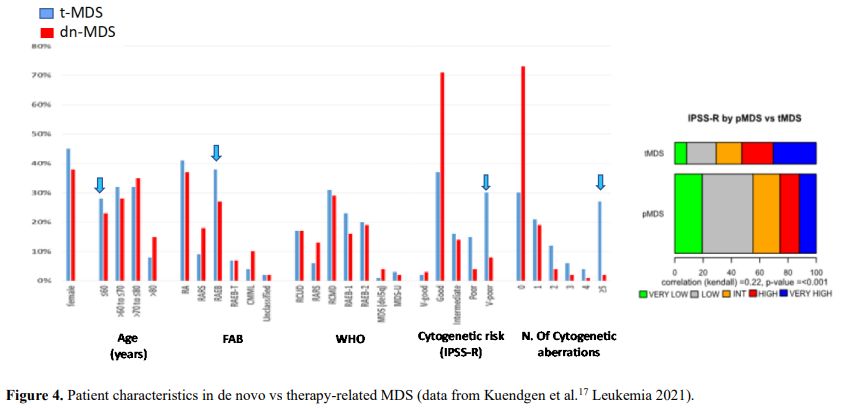
It is also very significant to notice that the prognosis of both MDS de novo and therapy-related can be evaluated by the same scoring systems.[8,14-17] Of the different methods of stratifying t-MDS, the best seems to be the IPSS-R (International Prognostic Scoring System, Revised), which considers, in descending order, five major variables for evaluating clinical outcomes, including cytogenetic risk groups, marrow blast percentage, and depth of cytopenias (hemoglobin, platelet, and ANC levels, respectively), therefore, to affirm that all t-MDS patients have an unfavorable prognosis is not valid. In general, in the t-MDS series, the proportion of high-risk patients is higher.[8,14-17] Furthermore, in general, the survival of every category was lower for t-MDS; however, patients with IPSS and MPSS had a very low survival, not significantly different in both patients with t-MDS and with p-MDS.[15] In the study of Zeidan, patients with t-MDS had significantly inferior survival than p-MDS (median, 19 vs. 46 months, respectively, P=0.005), and patients with t-MDS had a higher prevalence of adverse prognostic factors such as poor risk cytogenetics and higher blast percentages. Although a less favorable clinical outcome occurred in each t-MDS subset compared with p-MDS subgroups, FAB and WHO-classification, IPSS-R, and WPSS-R (WHO-based Prognostic Scoring System-revised) effectively separated t-MDS patients into different risk groups, indicating that all established risk factors for p-MDS maintained relevance in t-MDS, with cytogenetic features having enhanced predictive power. Thus there is significant heterogeneity in clinical outcomes in t-MDS with a small subset of patients having a more indolent disease course, who might not necessarily benefit from aggressive therapeutic interventions.[15,16] All this was confirmed in a large and multicenter study[17] where the predictive power of IPSS-R was almost comparable top-MDS in patients with a solid tumor as primary disease as well as in patients after radiotherapy only. However, the predictive power was lower in patients with a history of hematologic disease treated with chemotherapy. It is important to highlight that this extensive work demonstrated an unexpectedly high percentage of good-risk and normal cytogenetics, concordantly with other more recently published data[8,15,16] Figure 1, 2.
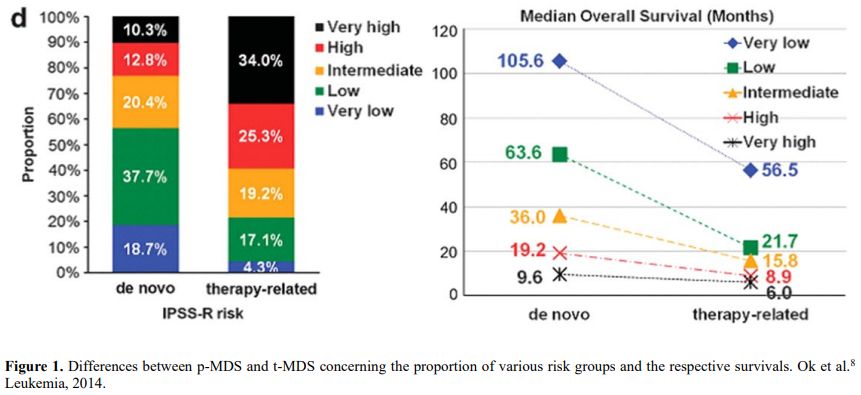 |
Figure 1. Differences between p-MDS and t-MDS concerning the proportion of various risk groups and the respective survivals. Ok et al.[8] Leukemia, 2014. |
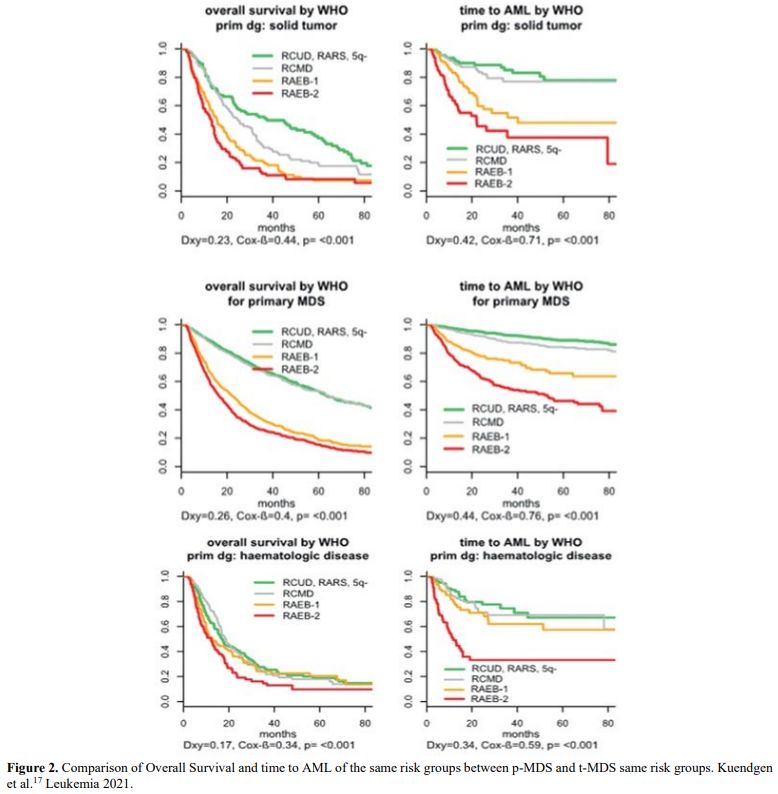 |
Figure 2. Comparison of Overall Survival and time to AML of the same risk groups between p-MDS and t-MDS same risk groups. Kuendgen et al.[17] Leukemia 2021. |