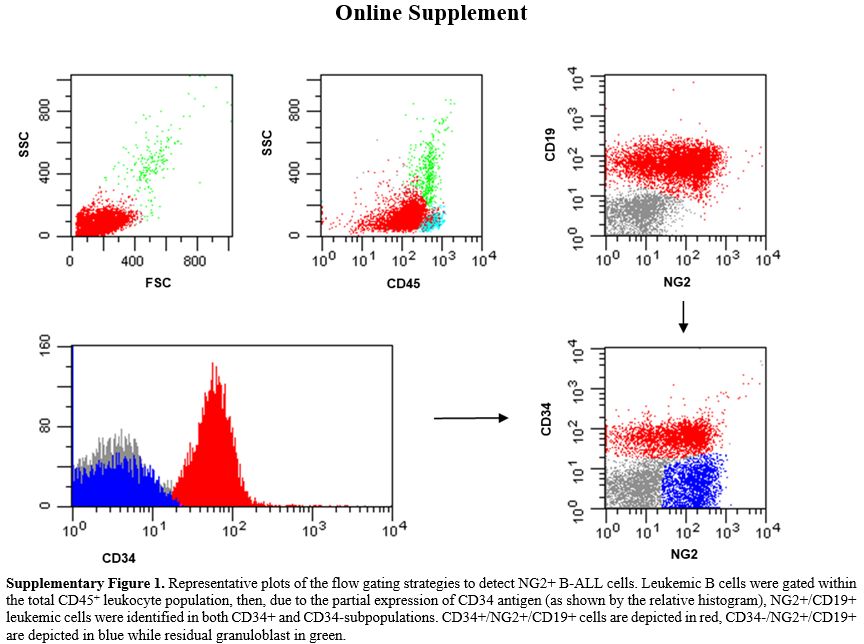
Only 2 pro-B ALLs with KMT2A-r showed low NG2 expression (<below the 10%) positivity cut-off, being equal to 4% and 5%, probably due to the steroid therapy administered to these patients before diagnostic work-up. The remaining 3/88 NG2+ B-ALLs (3.4%) did not harbor KMT2A-r– (1 pro-B and 2 B-common ALLs).
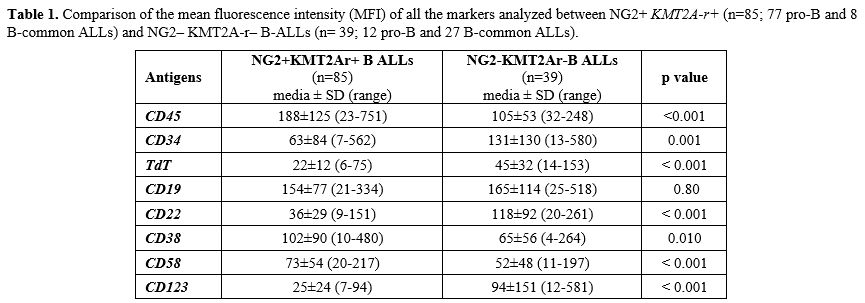
Antigen detection and surface expression intensity. To evaluate if the presence of KMT2A-r was associated with a distinctive immunophenotypic profile, beyond NG2+ B-ALLs, we analyzed and compared the MFI of CD45, TdT, CD34, CD19, CD20, CD22, CD38, CD58 and, CD123 antigens in NG2+ KMT2A-r + (n=85; 77 pro-B and 8 B-common ALLs) and NG2– KMT2A-r – B-ALLs (n= 39; 12 pro-B and 27 B-common ALLs). As shown in Table 1. In addition, to exclude any influence of the B-ALLs EGIL subtype on the peculiar immunophenotypic profile of KMT2Ar+ cases, we compared the expression intensity of all the markers analyzed, amongst the same subtype of B-ALLs (Table 2). Most of the markers analyzed (7/9, 77.8%) were differently expressed between the two categories. CD45 was expressed in all cases: MFI values were significantly higher in KMT2A-r+ than KMT2A-r– B-ALL regardless of the EGIL immunologic subtypes. CD34 was partially expressed in KMT2Ar+. More specifically, KMT2Ar+ B-ALLs were characterized by a significantly lower percentage of CD34+ blasts, as well as MFI, respect to KMT2Ar– samples independently from the EGIL subtype. In addition, among our cases, CD34 MFI appeared significantly lower in the presence of KMT2Ar, independently from the B-ALLs EGIL immunologic subtype (Table 2). TdT was expressed in all cases of B-lineage ALL. In particular, KMT2Ar+ B-ALL showed a significant downmodulation of TdT MFI compared to KMT2Ar– cases. This evidence was also confirmed within the same immunologic EGIL subtypes (KMT2Ar+ vs KMT2Ar– pro-B ALL) (Table 2).
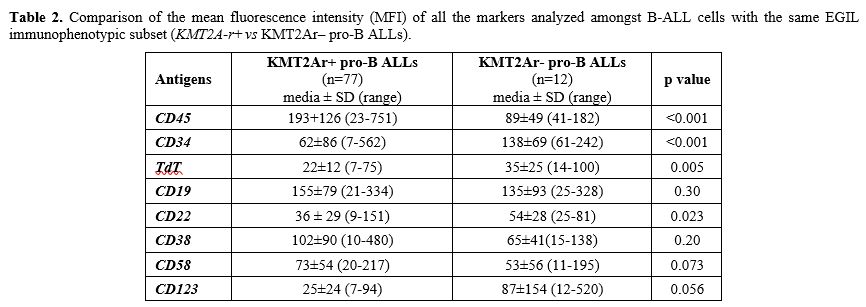 |
Table 2. Comparison of
the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of all the markers analyzed
amongst B-ALL cells with the same EGIL immunophenotypic subset
(KMT2A-r+ vs KMT2Ar– pro-B ALLs). |
CD19 and CD22, both targetable antigens, were expressed in all cases; interestingly CD19 was equally expressed in terms of both percentage and MFI regardless of KMT2A-r status; at variance, CD22 MFI values were significantly lower in KMT2Ar+ than KMT2Ar– B-ALLs, thus at least explaining the suboptimal efficacy of inotuzumab in this set of patients.[16]
CD38 was positive in all B-ALLs studied, and its MFI was significantly higher in (KMT2A-r+ vs KMT2A-r–: 102±90 vs 65±56, p=0.010). Finally, CD58 MFI appeared higher in KMT2Ar+ B-ALL (KMT2Ar+ vs KMT2Ar–: 73±54 vs 52±48, p< 0.001) while CD123, the interleukin-3 (IL-3) receptor α-chain, another antigen useful in MRD, had a lower MFI in KMT2Ar (KMT2Ar+ vs KMT2Ar–: 25±24 vs 94±151, p< 0.001).
Two additional markers were also evaluated: CD15 was evaluated in 48/88 NG2+ cases (43 KMT2A::AFF1+ pro-B, 3 KMT2A::AFF1+ B-common and 2 KMT2A::MLLT1+ pro-B ALLs) and detected in in 16/48 NG2+ cases (CD15+ B-ALLs: 72.06±24.40%, range 26-90%; CD15 MFI: 78.16±53.4, range 20-190); CD133 (Prominin-1), , was again studied in 48/88 NG2+ cases (43 KMT2A::AFF1+ pro-B, 3 KMT2A::AFF1+ B-common and 2 KMT2A::MLLT1+ pro-B ALLs) and was detected in all cases. with a mean percentage of positive cells of 84.37 ±11.64 (range 55-97%) and a mean MFI of 92.42±45.29 (range 18-190), suggesting a strong association of CD133 expression with NG2 positivity and the presence of KMT2Ar, mainly in the pro-B EGIL subtype.
Moreover, no differences in any of the antigens analysed were observed comparing KMT2Ar+ (n=8) vs KMT2Ar– (n=27) B-common ALLs, probably due to the low number of KMT2Ar+ cases characterized by this subtype (Table 3). In addition, no differences emerged in terms of antigen expression between KMT2Ar– pro-B ALLs and KMT2Ar– B-common ALLs, confirming the key role played by the presence of KMT2Ar in the peculiar phenotype of KMT2Ar+ leukemic cells (Table 4).
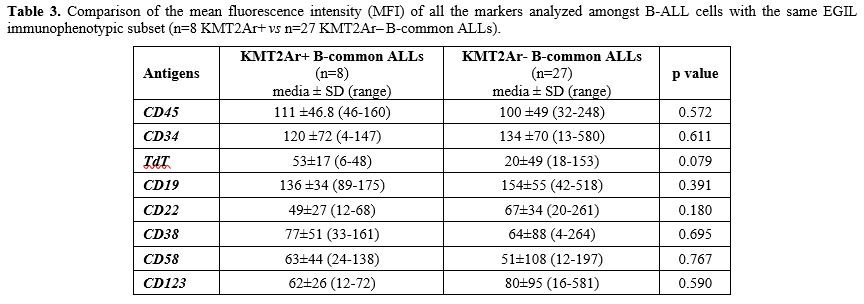 |
Table 3. Comparison of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of all the markers analyzed amongst B-ALL cells with the same EGIL immunophenotypic subset (n=8 KMT2Ar+ vs n=27 KMT2Ar‒ B-common ALLs). |
 |
Table 4.
Comparison of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of all the markers
analyzed amongst B-ALL cells without KMT2Ar (n=12 KMT2Ar‒ pro-B vs n=27
KMT2Ar– B-common ALLs). |