From January 2022 to June 2023, 109 NDTE MM patients from [4] haematology institutions with symptomatic disease, according to the International Myeloma Working Group criteria,[4] received Dara-VTD induction according to the approved doses and schedule. The historical control group consisted of 100 consecutive patients treated with VTD induction in the years 2006-2017.[5] Mobilizing therapy consisted of cyclophosphamide 1-3 gr/sqm followed by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) 10 mcg/kg starting the 5th day after that, with HSC harvest planned on the 11th day. Mobilizing cyclophosphamide was administered as outpatient and was well tolerated. Patients received only G-CSF 10 mcg/kg if they were older than 70 years or had renal impairment (i.e., eGFR < 50 ml/min). HSC collection target was 8 x 10^6/Kg, giving the possible need for a double ASCT. Poor mobilizer was defined as having < 20 CD34+/µL in peripheral blood on the 11th day after cyclophosphamide or, for patients receiving G-CSF only, on the fourth day of G-CSF administration. In that case, plerixafor was added at the standard dose of 0.24 mg/kg (0.16 mg/kg in case of renal impairment). Post-transplant engraftment was defined as the first of 3 consecutive days of an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) > 500/μL and platelets > 20,000/μL, without transfusion or G-CSF requirement. Data were collected in the context of a prospective observational study on lymphoproliferative disorders, currently ongoing in Bergamo Hospital and approved by the Bergamo Hospital’s Ethics Committee.
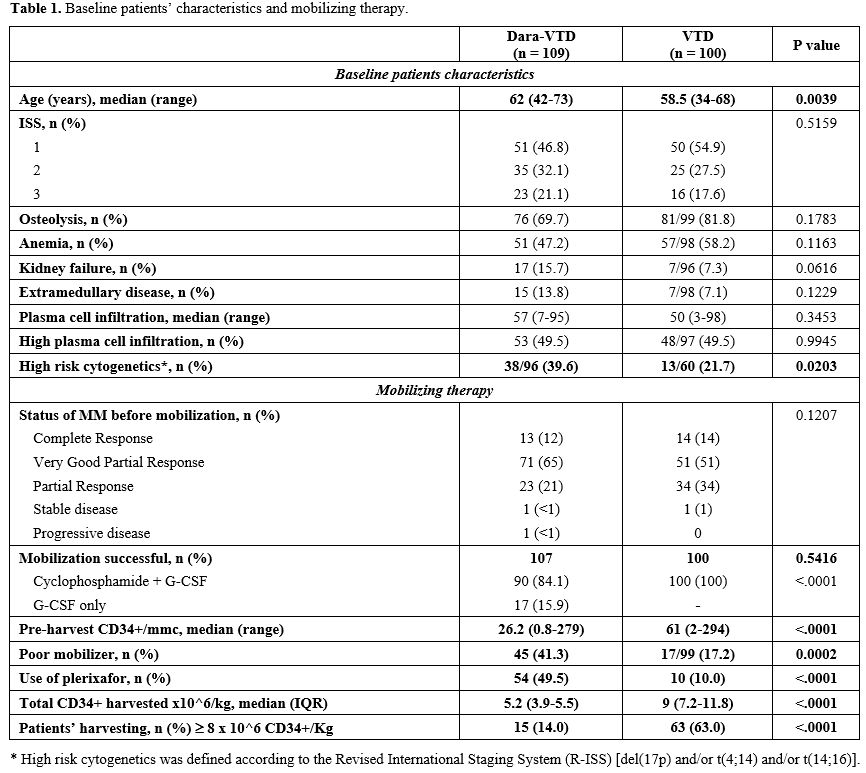
Most patients received the four planned induction cycles (106/109 patients of the Dara-VTD group vs 89/100 patients of the VTD groups). 77% of patients receiving Dara-VTD achieved a very good partial remission or a complete remission, as compared to 65% of patients receiving VTD (OR 1.76, 95% CI 0.96-3.26). Table 1 summarizes the baseline characteristics of the two study groups and mobilizing therapies.
93/109 patients of the Dara-VTD group received cyclophosphamide; among them, two patients had failed a previous G-CSF mobilizing therapy, even with the addition of plerixafor, whereas the other 16 patients received G-CSF only. In the VTD group, all patients received cyclophosphamide.
 |
|
The pre-harvest median number of CD34+/μL in the Dara-VTD group was 26 (range 0.8-279) vs 63 (range 2-294) in the VTD group, and the incidence of poor mobilizers was 41.3% vs 17.2%, respectively (OR 3.39, 95% CI 1.8-6.61, p = 0.0002). The addition of daratumumab was not associated with a delayed peak of CD34+ pre-harvest.
In the Dara-VTD group, all patients who developed hematologic toxicity during induction turned out to be poor mobilizers (OR 3.5, 95% IC 1.36-9.59, p = 0.011).
Plerixafor was used in 54/109 patients in the Dara-VTD group vs. ten patients in the VTD group. In the Dara-VTD group, all patients that received G-CSF only resulted in poor mobilizers and required plerixafor before HSC harvest; therefore, cyclophosphamide showed to be superior with regards to G-CSF as mobilizing therapy (p = 0.011). In the Dara-VTD group, two patients failed HSC mobilization, whereas no mobilization failure was registered among the VTD group. The median number of collected HSC was significantly lower in the Dara-VTD group vs VTD group: 5.2 x 10^6/Kg (IQR 3.9-5.5) vs 9.0 x 10^6/kg (IQR 7.2-11.8), respectively (p < 0.0001).
At data cut-off, the first transplant had been performed in 100/107 Dara-VTD group patients; six patients were still waiting for the procedure, and one patient experienced disease progression after the HSC harvest. Three out of the 100 VTD group patients did not undergo autologous transplant, because of medical decision. Patients receiving Dara-VTD had a slower median time to neutrophils and platelets engraftment (13 vs 11 days in the VTD group, p< 0.0001). However, we did not observe any difference in terms of infection incidence. Notably, post-transplant infection incidence in the Dara-VTD group was 43%, mostly febrile neutropenia. Although the second transplant was planned for 36 patients treated with Dara-VTD, it was performed in only ten patients, mainly because of insufficient HSC harvest.
Our experience confirms that the addiction of daratumumab to VTD increased the number of patients reaching a good response by the end of induction. It also confirms that Dara-VTD is associated with an increased number of poor mobilizers, higher use of plerixafor, and lower collected HSC. These findings were already outlined by the Authors of the CASSIOPEIA trial, which showed that patients receiving Dara-VTD harvested a significantly lower number of HSC and required plerixafor administration in 21.7% of patients versus 7.9% of patients in VTD arm.6 In our real-life experience, approximately half of the Dara-VTD group patients received Plerixafor. Such a high prevalence is due to the administration of plerixafor also to patients who, although not poor mobilizers in the narrow sense, had a number of CD34+/μL just above the cut-off value of 20.
Conversely, among the VTD group, the number of patients receiving plerixafor was lower than that of the poor mobilizers because plerixafor became available in Italy only at the end of 2011, which excluded seven patients from receiving this drug. As shown in Table 1, there is a slight, although significant, difference in patients' age between the two groups and this could play a role in determining poor mobilizing events. Remarkably, the CASSIOPEIA trial enrolled patients up to the age of 65 years, so the impact of frontline Daratumumab in an older population, in terms of HSC mobilization and collection, should be further assessed in real-life analysis.
Data on stem cell collection from other pivotal trials, namely MASTER and GRIFFIN, which adopted a lenalidomide-based induction therapy, confirmed a lower HSC collection in patients receiving daratumumab.[7] However, lenalidomide itself is deemed to have an impact on HSC mobilization and collection, unlike thalidomide. Concerning the choice of the mobilizing therapy, in our study, cyclophosphamide doses varied between 1.5-3 gr/sqm, according to local practice; we were not able to compare the impact of different doses of cyclophosphamide on HSC collection because of a low number of patients who received 3 gr/sqm. A recent report showed that using 4 gr/sqm with on-demand plerixafor is feasible and could overcome the negative impact of daratumumab on HSC harvest.[8] We observed slower post-ASCT engraftment in patients receiving Dara-VTD, with a subsequent longer duration of hospitalization but not a greater incidence of infection. The lower HSC harvest in the Dara-VTD patients hampered the possibility of a second ASCT for most patients who could have benefited from it, according to the indication provided by EHA/ESMO and NCCN guidelines.[9]
The principal limitations of this study are its retrospective nature and the relatively short follow-up, which did not allow us to assess whether a poor mobilizing event could have an impact on post-ASCT clinical outcomes.
In conclusion, our experience with Dara-VTD confirms a higher incidence of poor mobilizers and a lower number of harvested HSC when compared to a cohort of patients receiving VTD. In these patients, cyclophosphamide-based mobilizing therapy, with on-demand plerixafor, should be adopted whenever possible. Despite the lower number of collected HSC, almost all patients were able to undergo the ASCT without increased incidence of infectious complications. Only a minority of high-risk patients could receive a double ASCT, whose role in a modern first-line therapy based on quadruplets and post-ASCT should be further investigated.